Profile

|
Publications
Multidimensional Byte Pair Encoding: Shortened Sequences for Improved Visual Data Generation

In language processing, transformers benefit greatly from text being condensed. This is achieved through a larger vocabulary that captures word fragments instead of plain characters. This is often done with Byte Pair Encoding. In the context of images, tokenisation of visual data is usually limited to regular grids obtained from quantisation methods, without global content awareness. Our work improves tokenisation of visual data by bringing Byte Pair Encoding from 1D to multiple dimensions, as a complementary add-on to existing compression. We achieve this through counting constellations of token pairs and replacing the most frequent token pair with a newly introduced token. The multidimensionality only increases the computation time by a factor of 2 for images, making it applicable even to large datasets like ImageNet within minutes on consumer hardware. This is a lossless preprocessing step. Our evaluation shows improved training and inference performance of transformers on visual data achieved by compressing frequent constellations of tokens: The resulting sequences are shorter, with more uniformly distributed information content, e.g. condensing empty regions in an image into single tokens. As our experiments show, these condensed sequences are easier to process. We additionally introduce a strategy to amplify this compression further by clustering the vocabulary.
Quantised Global Autoencoder: A Holistic Approach to Representing Visual Data

In quantised autoencoders, images are usually split into local patches, each encoded by one token. This representation is redundant in the sense that the same number of tokens is spend per region, regardless of the visual information content in that region. Adaptive discretisation schemes like quadtrees are applied to allocate tokens for patches with varying sizes, but this just varies the region of influence for a token which nevertheless remains a local descriptor. Modern architectures add an attention mechanism to the autoencoder which infuses some degree of global information into the local tokens. Despite the global context, tokens are still associated with a local image region. In contrast, our method is inspired by spectral decompositions which transform an input signal into a superposition of global frequencies. Taking the data-driven perspective, we learn custom basis functions corresponding to the codebook entries in our VQ-VAE setup. Furthermore, a decoder combines these basis functions in a non-linear fashion, going beyond the simple linear superposition of spectral decompositions. We can achieve this global description with an efficient transpose operation between features and channels and demonstrate our performance on compression.
Awards:
@inproceedings{10.2312:vmv.20251231,
booktitle = {Vision, Modeling, and Visualization},
editor = {Egger, Bernhard and Günther, Tobias},
title = {{Quantised Global Autoencoder: A Holistic Approach to Representing Visual Data}},
author = {Elsner, Tim and Usinger, Paula and Czech, Victor and Kobsik, Gregor and He, Yanjiang and Lim, Isaak and Kobbelt, Leif},
year = {2025},
publisher = {The Eurographics Association},
ISBN = {978-3-03868-294-3},
DOI = {10.2312/vmv.20251231}
}
Retargeting Visual Data with Deformation Fields
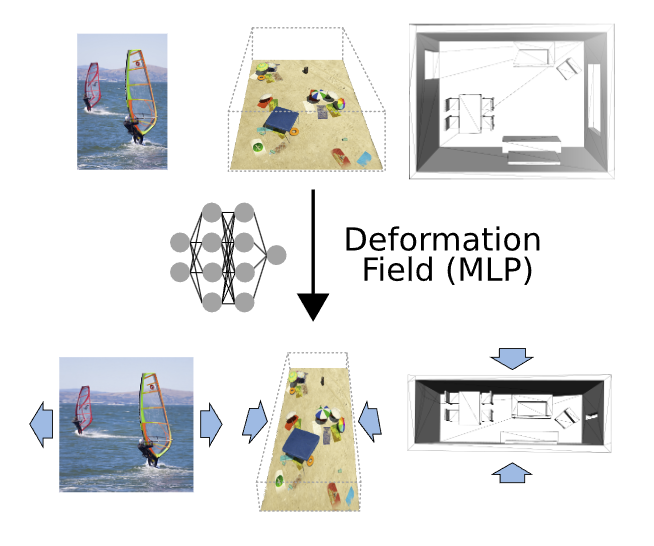
Seam carving is an image editing method that enables content- aware resizing, including operations like removing objects. However, the seam-finding strategy based on dynamic programming or graph-cut lim- its its applications to broader visual data formats and degrees of freedom for editing. Our observation is that describing the editing and retargeting of images more generally by a deformation field yields a generalisation of content-aware deformations. We propose to learn a deformation with a neural network that keeps the output plausible while trying to deform it only in places with low information content. This technique applies to different kinds of visual data, including images, 3D scenes given as neu- ral radiance fields, or even polygon meshes. Experiments conducted on different visual data show that our method achieves better content-aware retargeting compared to previous methods.
Intuitive Shape Editing in Latent Space
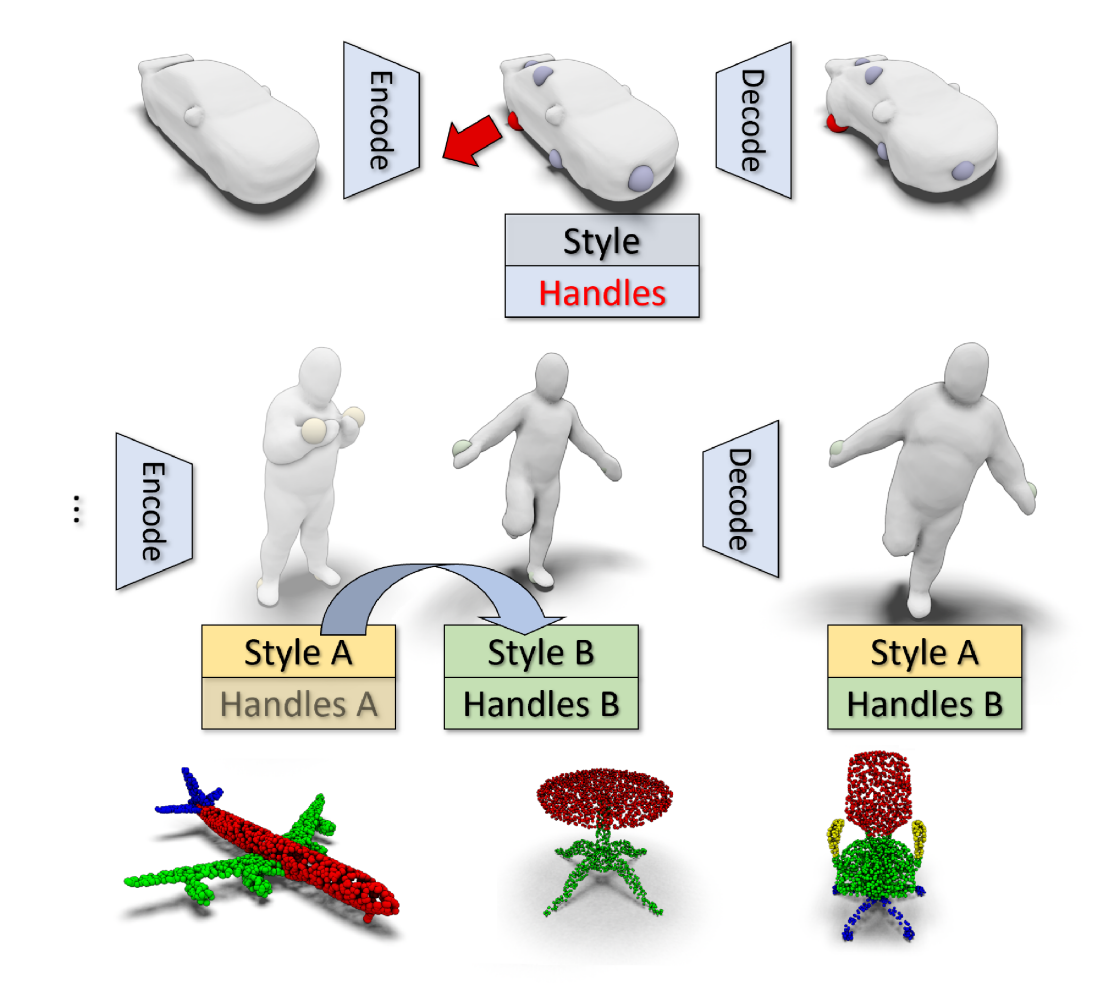
The use of autoencoders for shape editing or generation through latent space manipulation suffers from unpredictable changes in the output shape. Our autoencoder-based method enables intuitive shape editing in latent space by disentangling latent sub-spaces into style variables and control points on the surface that can be manipulated independently. The key idea is adding a Lipschitz-type constraint to the loss function, i.e. bounding the change of the output shape proportionally to the change in latent space, leading to interpretable latent space representations. The control points on the surface that are part of the latent code of an object can then be freely moved, allowing for intuitive shape editing directly in latent space. We evaluate our method by comparing to state-of-the-art data-driven shape editing methods. We further demonstrate the expressiveness of our learned latent space by leveraging it for unsupervised part segmentation.
Highly accurate digital traffic recording as a basis for future mobility research: Methods and concepts of the research project HDV-Mess
The research project HDV-Mess aims at a currently missing, but very crucial component for addressing important challenges in the field of connected and automated driving on public roads. The goal is to record traffic events at various relevant locations with high accuracy and to collect real traffic data as a basis for the development and validation of current and future sensor technologies as well as automated driving functions. For this purpose, it is necessary to develop a concept for a mobile modular system of measuring stations for highly accurate traffic data acquisition, which enables a temporary installation of a sensor and communication infrastructure at different locations. Within this paper, we first discuss the project goals before we present our traffic detection concept using mobile modular intelligent transport systems stations (ITS-Ss). We then explain the approaches for data processing of sensor raw data to refined trajectories, data communication, and data validation.
@article{DBLP:journals/corr/abs-2106-04175,
author = {Laurent Kloeker and
Fabian Thomsen and
Lutz Eckstein and
Philip Trettner and
Tim Elsner and
Julius Nehring{-}Wirxel and
Kersten Schuster and
Leif Kobbelt and
Michael Hoesch},
title = {Highly accurate digital traffic recording as a basis for future mobility
research: Methods and concepts of the research project HDV-Mess},
journal = {CoRR},
volume = {abs/2106.04175},
year = {2021},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.04175},
eprinttype = {arXiv},
eprint = {2106.04175},
timestamp = {Fri, 11 Jun 2021 11:04:16 +0200},
biburl = {https://dblp.org/rec/journals/corr/abs-2106-04175.bib},
bibsource = {dblp computer science bibliography, https://dblp.org}
}

